TPLO Surgery for Dogs
The most common traumatic orthopedic injury in dogs of all ages and breeds is a tear of the cranial cruciate ligament, or CCL. By the late 1990s, TPLO surgery for dogs, or tibial plateau leveling osteotomy, became a common technique to address the condition due to its significant success in large and active canine patients. This revolutionary approach for dog knee surgery redefines the tibial plateau's angle, ensuring stability in the knee joint without relying on the damaged ligament.
Anatomy of the Stifle Joint
The cruciate ligaments are important stabilizing elements within the canine stifle joint, or knee. There are two cruciate ligaments, one anterior and one posterior, which are the cranial and caudal cruciate ligaments, respectively. Both canines and humans commonly injure their cranial cruciate ligaments, though we know this ligament better as the anterior cruciate ligament in humans.
About TPLO or ACL Surgery
Early signs of CCL stress or partial rupture in canines include stiffness or mild lameness. Symptoms increase as the CCL tears further, and a full tear usually results in marked lameness in the affected leg. In some cases, the knee will make a clicking or popping sound as the dog walks. This can indicate damage to the cartilage cushions within the knee. A dog with a torn ACL will suffer from sharp stifle instability. Veterinarians often describe this instability as cranial tibial thrust or “drawer” movement. This shearing motion causes excessive wear of the cartilage on the ends of the bones within the joint, and stretches the surrounding tissues, causing pain, and the best solution is a dog ACL repair. It can also injure the medial meniscus within the stifle. The tibial plateau leveling osteotomy procedure can eliminate excessive tibial thrust, thus creating a more functionally stable joint and sound gait.
Diagnosis and Procedure
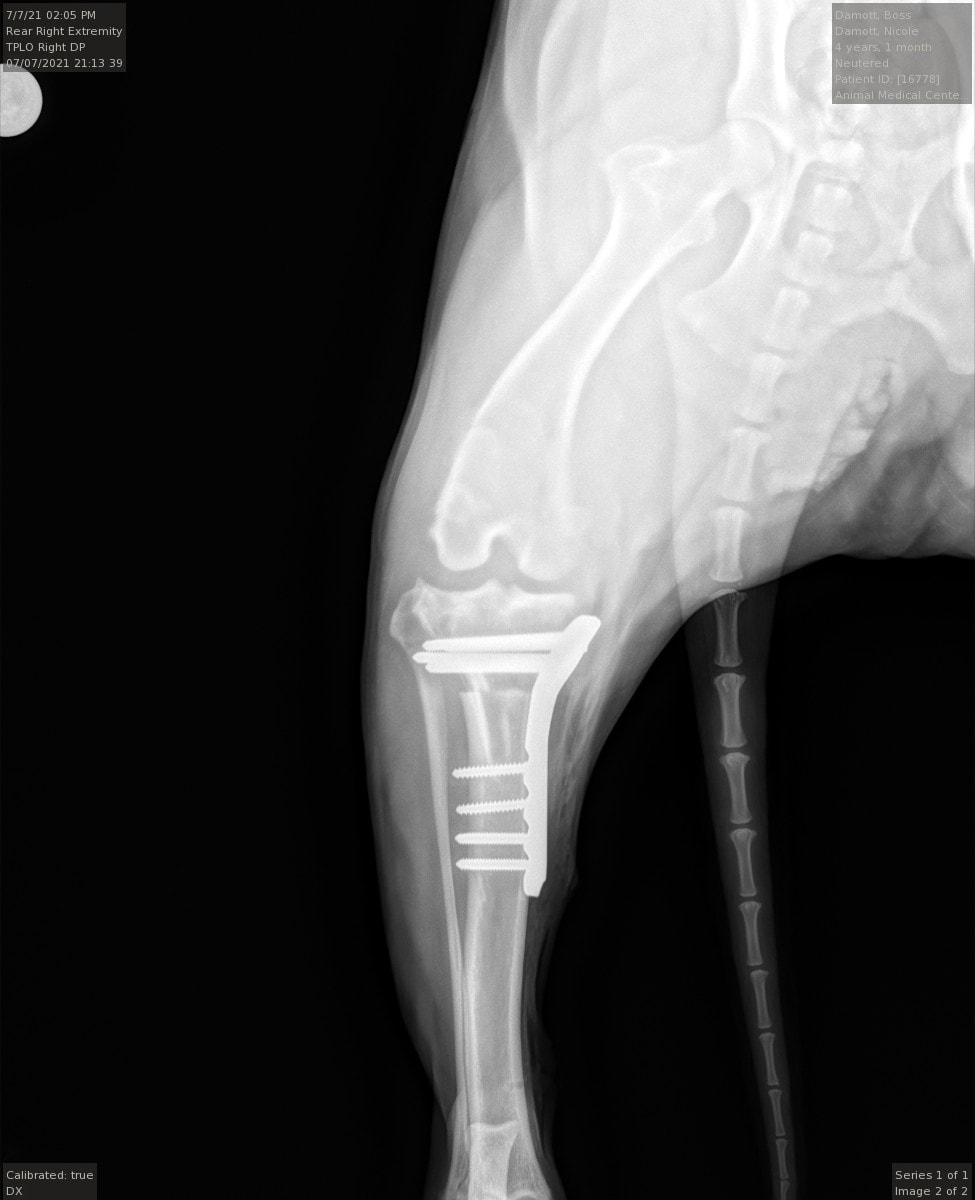
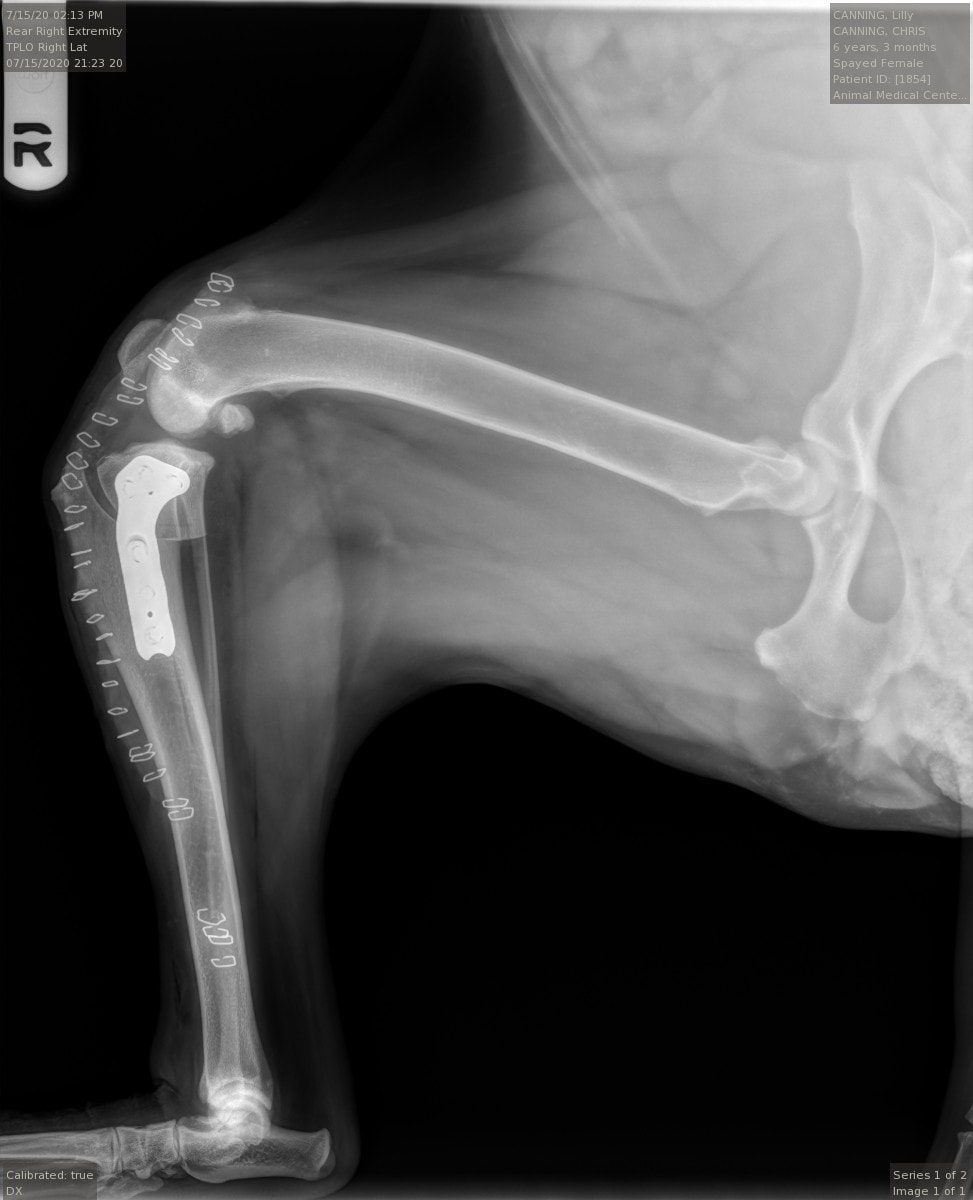
We diagnose a CCL tear by feeling and X-raying the knee. While the radiograph will not show the CCL itself, radiography will indicate osteoarthritic changes and joint swelling. To perform ACL surgery for dogs, a specially designed blade makes a curved cut through the tibia. Surgeons then precisely rotate the top portion of the tibia to level the slope of the tibial plateau and prevent the instability and sliding that occurs with a CCL tear. A bone plate and screws are then placed on the tibia to stabilize it and allow healing to occur.
Outcome and Prognosis
Reports consistently indicate that dogs that undergo TPLO or ACL surgery have an excellent functional outcome and decreased development of osteoarthritis. With TPLO surgery for dogs, it’s possible to return your dog to nearly normal long-term function following CCL rupture, which has not been the typical expectation with any of the traditional techniques attempted before. A potential reduction in the progression of arthritis is an additional benefit. Strict confinement will be crucial for several weeks after surgery to avoid potential difficult complications, which you’ll discuss further during your appointment with the surgeon.
By scheduling your dog’s TPLO surgery with us, you're choosing a team that’s dedicated to superior outcomes. Our expertise, coupled with our advanced surgical techniques, ensures a quicker, more reliable recovery. Contact us today to learn more about this surgery. You can trust us to provide the compassionate, specialized care your pet deserves.
Anatomy of the Stifle (knee)
"Cornell University Veterinary Specialists"
https://www.cuvs.org/sites/default/files/documents-2017-01/cuvs-client-info-sheet-tibial-plateau-leveling-osteotomy.pdf